Climate- and Water protection for the Earth.
Clean and Save the World e.V was founded with the mission to reduce or even clean up harmful agents such as plastics, both found as nano- and microplastic; fuels of all kind, as well as chemicals and heavy metals found to reduce their harmful effects in seas and on land. For this we are using the most modern environmental technologies and methods. By cleaning up harmful agents in the oceans, lakes, rivers, seas, channels, and harbours, balance is brought to our environment and its biology. For this we need lakes and oceans, not only as places of sightseeing and as vacation spots but also ordinarily for our daily lives. Many plankton organisms inhabit our oceans, producing half of the oxygen that we breath. Additionally, lakes absorb up to 90% of sun energy and binds circa 30% of carbon dioxide to regulate the climate.
Our ecosystem is throughoutly damaged.
Whether in the deep sea, or in the tropical regions of the north- and east seas. At each coast of the world plastic waste products are found.
In the oceans drift at least 150 million tons of plastic waste. This is equal to the weight of 15,000 eiffeltowers or half of the world population. Every year circa 10 million tons are added. These massive amounts of plastic waste arrive through the rivers of Asia, Europe, the USA and Canada into the lakes and oceans. Through the ocean currents massive amounts of plastic waste are gathered in the ocean. In total, it is assumed that there exist five garbage patches, with a sixth one forming in Antarctica.
The biggest garbage patch is located in the Pacific Ocean is about the size of Middle Europe.
Mit dem Laden des Videos akzeptieren Sie die Datenschutzerklärung von YouTube.
Mehr erfahren
The biggest environmental problem of our time in regards to climate- und water protection.
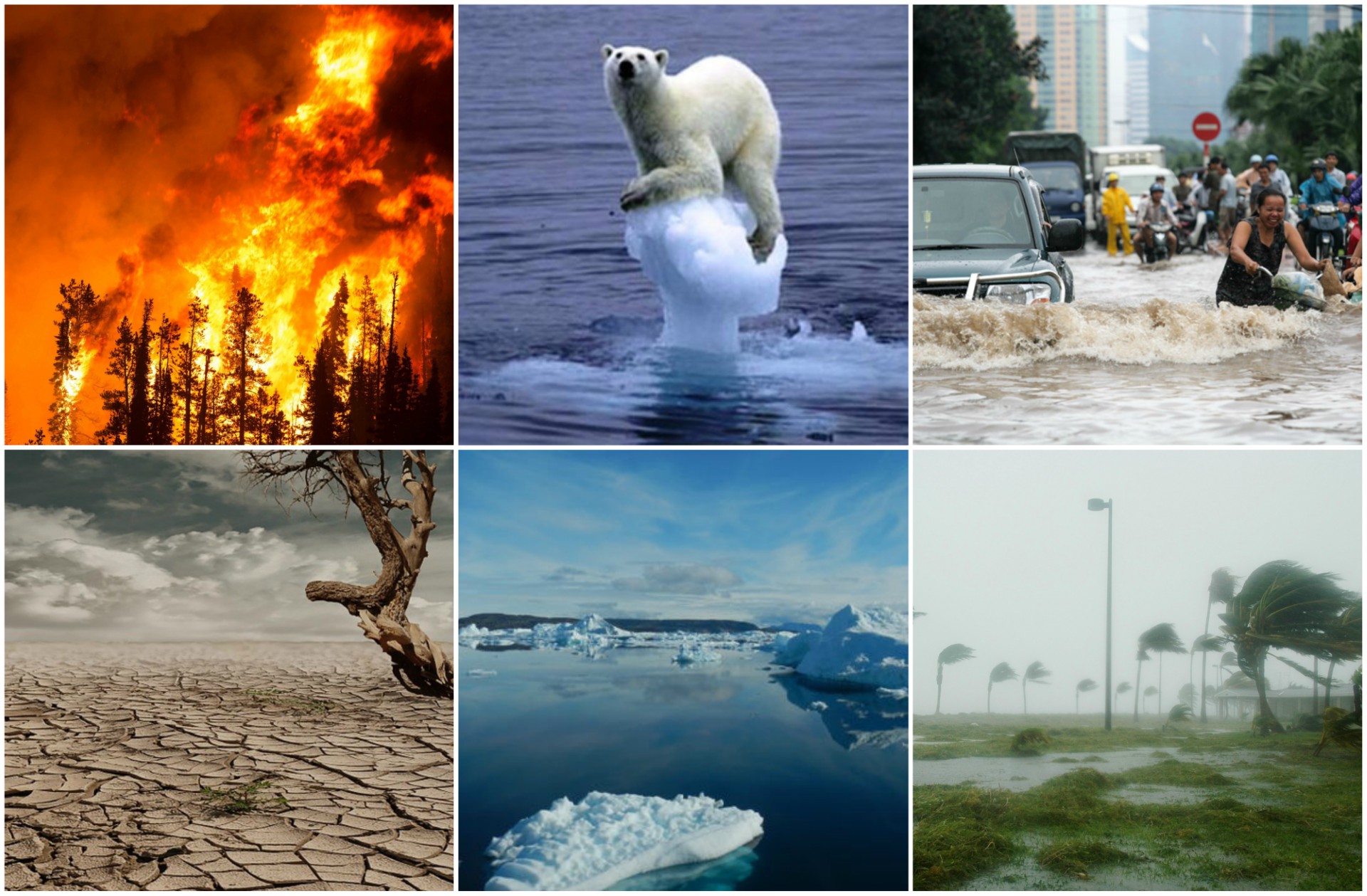

- Weather extremes such as heat burns and droughts, heavy rain, floods and cyclones are all becoming more frequent. The consequences of climate change are felt worldwide. Especially in water these effects are most apparent, often in connecting with of areas suffering from too much or too little water supplies and worsening water quality.
- The polar caps are melting. The water levels are rising worldwide at an alarming and environmentally damaging rate.
- Our lakes are overflowing with plastic waste which cause the Gulf Stream to be slowed down, it being critical to ocean life. By now plastic particles are found in the bodies of 50% of all fish in the Mediterranean Sea and 80% of fish larvae in river deltas in the European Union. These plastic particles arrive in the human food chain.
- As plastic particles bind many toxic chemicals to themselves, it can, for example, be the cause for various cancers in the organism of humans and other animals.
- Plastic in the human body can lead to damages in genetic material, inflammation, organ damage and increased rates of heart attacks and strokes. Plastic substances have already been found inside the human heart.
- The water which is the foundation of life and that of future generations is systematically endangered.
- Das Meer ist inzwischen einer der dreckigsten Orte der Welt. Deutschland ist Müll-Europameister.
- Even in the animal kingdom drastic consequences are becoming apparent. Due to the global waste catastrophy, over 700 animals species are directly endangered. Every year millions of sea birds and a hundred thousand sea mammals die as a result of excess waste in our environment.
- The overwhelming flood of plastics cannot be processed by the environment. For example, a plastic bottle could remain in the environment or seas for 250 years, e.g forever.
- “Plastic does not break apart, but only becomes smaller. One piece of plastic waste, (for example, Polyethylene), the size of a sugar cube, in the course of time breaks into circa 1500 microparticles, (with a diameter of 10 μm), or circa 150,000 nanoparticles (a diameter of 100 μm). It is the rule, that the smaller the plastic particle, the more problematic it becomes, as nanoparticles easily enter into human cells. (For example, the SARS-CoV 2 virus has a size of 60 to 90 nanometers.) Additionally, nanoplastics possess an extremely big specific surface to which harmful substances and heavy metals can bind themselves to and enter into the organism. According to estimates, every human ingests up to five grams of microplastics weekly through their food. As many as for a credit card.” (Source: FAU Friedrich-Alexander-University Erlangen Nuremberg)
Seagrass beds, mangroves, and coral reefs are climate-regulating CO₂ carbon sinks. They store over 50% of CO₂ and are threatened worldwide.
“The ecosystem services provided by seagrass beds are phenomenal, but continue to be underestimated. Seagrass beds are of enormous ecological and economic importance. They are perhaps the most potent natural carbon sink. They provide habitat for many thousands of animal species such as crabs and mussels. For others, such as sea turtles, manatees, etc., seagrass is a food source. Seagrass beds act as breakwaters in the natural coastal protection system and, as biofilters, also cleanse seawater of pathogenic germs. And that’s not all,” explains biologist Ulrich Karlowski from the German Foundation for Marine Conservation (DSM)
Seagrass grows in the Baltic Sea at depths of 2 to 7 meters. In the Mediterranean, thanks to good light conditions, it can even be found at depths of up to 50 meters and grow to a length of up to 2 meters. The plants can live for several hundred years (Neptune grass even over 1,000 years). There are 65 known species of seagrass, 22 of which are critically endangered.
Seagrasses can absorb nutrients and water from the seabed with the help of their roots. They perform photosynthesis via their leaves. In doing so, they absorb CO₂ carbon dioxide from the seawater and convert it into sugar and oxygen with the help of sunlight.
Blue Carbon
Depending on their location and species, seagrass beds have a CO₂ reduction rate that is 30 to 50 times higher than forests. Depending on the species, one hectare of seagrass bed stores the same amount of carbon as ten hectares of forest, and does so 35 times faster.
Seagrass beds cover less than 0.2 percent of all oceans, seas, and rivers. In more than 150 countries on all continents, they store about 15 percent of the CO₂ in all oceans and seas, such as the Pacific Coast, Atlantic Ocean, Mediterranean Sea, Black Sea, North Sea, and Baltic Sea with their rivers.
Since much of the carbon is not only stored in living and dead plant parts, but also in the sediment via the rhizomes, the storage facilities can have a very long lifespan – up to thousands of years. The prerequisite is that they are not damaged or destroyed.

However, seagrass beds in the Mediterranean have shrunk by 13 to 50 percent since 1960. The Helsinki Commission has classified the seagrass beds in the Baltic Sea as highly endangered.
Up to seven percent of all seagrass beds disappear every year – equivalent to an annual loss of approximately the area of Lake Constance (12,000 square kilometers).
Reasons for the decline of seagrass include:
Rising temperatures, agricultural runoff and nutrient inputs, sea level rise, shipping accidents, and pollution from oil and other pollutants from leaks and industrial facilities.
Seagrasses are very sensitive to a number of environmental parameters. They react particularly strongly to excessive nutrient inputs. Too many nutrients, which are primarily carried into the sea via rivers, lead to overfertilization of the water and have a host of negative consequences for the entire ecosystem. The many nutrients have a directly toxic effect on seagrass.
They also increase algae growth, turning the water green, which means less light for seagrass.
Mechanical disturbances also threaten sensitive seagrasses, such as bottom trawling, ship and boat engines, anchors from boats and sailing ships, and changes in hydrodynamics, for example due to infrastructure development (LNG pipelines).
“For healthy oceans, for climate protection, and for the millions of people who depend on healthy and resilient coastal waters for food, recreation, livelihoods, or free coastal protection,” Karlowski emphasizes the global significance of UN World Seagrass Day.
Seagrass beds are not only a habitat for animals, but also an important carbon sink. Their complete loss could lead to the release of CO2 in the order of 10 gigatons (10 billion tons). “We must protect seagrass beds and restore them where they have been destroyed.”
Coral reefs and mangrove forests threatened
Coral reefs and mangrove forests are counted as the most productive ecosystems of our world outside of rainforests. They protect beaches and coasts from tsunamis and erosion while offering a habitat for thousants of animal spieces. Plastic waste in oceans worldwide threatens these unique habitats. Mangroves are especially efficent as carbon reservoirs. They can take in a large amount of carbon dioxide from the atmosphere, which is saved inside their biomass and sediment. The carbon which is stored inside of the mangrove sediment can remain stored there for hundreds or even thousands of years. Compared to other forest ecosystems of the Earth, mangroves are able to store four times as much carbon per square area. Thus, it provides an important role in the fight against climate change as natural carbon sinks.
In a total of 120 countries of the Earth, approximately 14 million hectars of mangrove are part of natural coastal vegetation.
Corals, like mangrove forests and seagrass meadows, are ecosystems that play a major role in mitigating climate change.
Plankton contaminated with micro- and nano plastics bind less carbon from the atmosphere. Thus, the function of the ocean and lakes as global carbon sinks are reduced. In the Mediterranean Sea it is estimated that every two plankton organisms contain a part of microplastic within them. A study from the GMIT shows that micro- and nano plastics have an impact on our climate.
“As a result of the fragmentation through ripples and UV-radiation, certain types of plastics, (mainly one-way plastic material such as packaging), release greenhouse gases. Mostly it is methane and ethylene. The impact of methane is especially severe as methane leads to a 34 times stronger greenhouse gas efect than carbon.”
Methane emissions from plastic particles are dependent on their size. Thus, a fine powder produces up to 500 times more methane than the same amount released as bigger particles. The smallest particles of nano plastics are carried over thousands of kilometers, even onto the Artic continent, where they mix into sea ice.
Even the mangrove forests, which serve as carbon sinks, and coral reefs are endangered by plastic waste substances.
Coral reefs belong to the most known ecosystem of the ocean. These especially sensitive and complex habitats have been named the rainforests of the ocean, thanks to their species variety. As nets and plastic bags cover corals, they suffer from less access to light and nutrients.
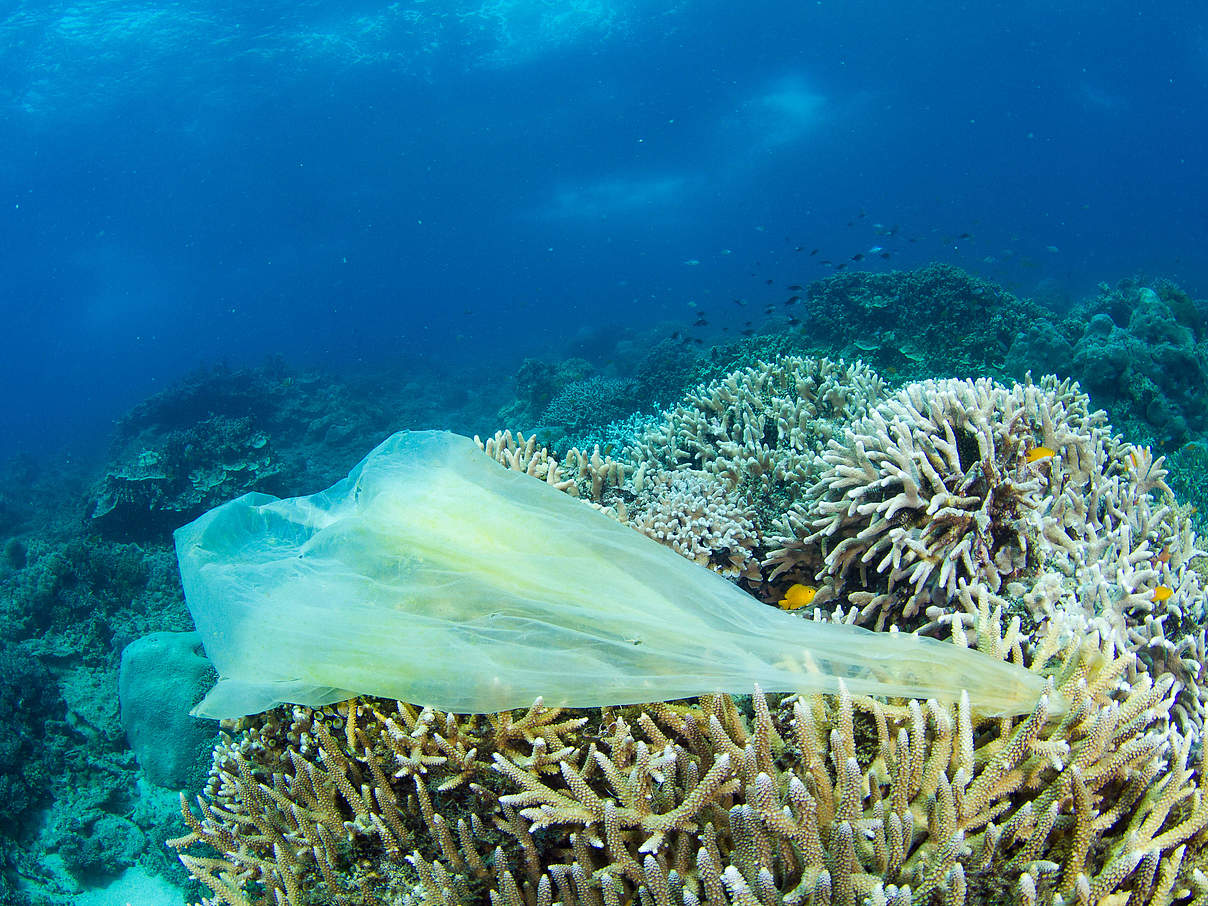

The rich sinking of carbon dioxide in the ocean as well as through mangrove forests is being severely hampered and disadvantaged by plastic waste, present as micro- and nano particles.
The property of the ocean to take in massive amounts of carbon dioxide has kept the Earth safe from a total collapse of its climate. Between 30 to 40 percent of the carbon dioxide released with fossil sources by humans are broken apart inside of the ocean. In theory, the ocean could store up to 80 percent of carbon dioxide. In reality, this would take at least a thousand years. This is because the higher the concentration of carbon dioxide in the ocean, it becomes more difficult for such a process to function over time. Additionally, a measurable slowing of the oceans circulation has blocked the intake of climate gases.
Plastics and greenhouse gas effects
A GMIT study shows that micro- and nanoplastics also have an impact on the climate.
“When certain types of plastic (mainly single-use plastics and packaging) fragment due to UV radiation, greenhouse gases are released. These are mostly methane and ethylene. The effect of methane is particularly significant.
Since methane has 34 times the greenhouse effect of carbon dioxide.” Methane emissions from plastic items are related to their size. For example, a fine powder produces almost 500 times more methane than the same amount of plastic in larger particles.
The tiniest nanoplastic particles are carried through the air thousands of kilometers to the Arctic, where they accumulate in the ice.
Let our blue planet become blue again!
The conditions of our waters is closely interlinked with the health of our climate. We need to act, otherwise in the year 2050 more plastic waste will be floating in the lakes as fishes and our climate are severely damaged.
At the same time we want bring awareness of the dangers of environmental pollution to the consciousness of mankind. Politicians are also called to prevent an increase in one-way plastics and to further observe the bio recyling of all plastics with the highest priority.
